Market News
How Central Banks Impact the Forex Market - DAILY FX
THE ROLE OF CENTRAL BANKS IN THE FOREX MARKET
Central banks are mainly responsible for maintaining inflation in the interest of sustainable economic growth while contributing to the overall stability of the financial system. When central banks deem it necessary they will intervene in financial markets in line with the defined “Monetary Policy Framework”. The implementation of such policy is highly monitored and anticipated by forex traders seeking to take advantage of resulting currency movements.
WHAT IS A CENTRAL BANK?
>span class="gsstx">Central Banks are independent institutions utilized by nations around the world to assist in managing their commercial banking industry, set central bank interest rates and promote financial stability throughout the country.
Central banks intervene in the financial market by making use of the following:
- Open market operations: Open market operations (OMO) describes the process whereby governments buy and sell government securities (bonds) in the open market, with the aim of expanding or contracting the amount of money in the banking system.
- The central bank rate: The central bank rate, often referred to as the discount, or federal funds rate, is set by the monetary policy committee with the intention of increasing or decreasing economic activity. This may seem counter-intuitive, but an overheating economy leads to inflation and this is what central banks aim to maintain at a moderate level.
Central banks also act as a lender of last resort. If a government has a modest debt to GDP ratio and fails to raise money through a bond auction, the central bank can lend money to the government to meet its temporary liquidity shortage.
Having a central bank as the lender of last resort increases investor confidence. Investors are more at ease that governments will meet their debt obligations and this heps to lower government borrowing costs.
FX traders can monitor central bank announcements via the central bank calendar
MAJOR CENTRAL BANKS
“The Fed” presides over the most widely traded currency in the world according to the Triennial Central Bank Survey, 2016. Actions of The Fed have implications not only for the US dollar but for other currencies as well, which is why actions of the bank are observed with great interest. The Fed targets stable prices, maximum sustainable employment and moderate long-term interest rates.
European Central Bank (European Union)
MAJOR CENTRAL BANKS
European central bank (ECB) is like no other in that it serves as the central bank for all member states in the European Union. The ECB prioritizes safeguarding the value of the Euro and maintaining price stability. The Euro is the second most circulated currency in the world and therefore, generates close attention by forex traders.
Bank of England
Bank of England operates as the UK’s central bank and has two objectives: monetary stability and financial stability. The UK operates using a Twin Peaks model when regulating the financial industry with the one “peak” being the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) and the other the Prudential Regulating Authority (PRA). The Bank of England prudentially regulates financial services by requiring such firms to hold sufficient capital and have adequate risk controls in place.
Bank of Japan
Bank of Japan has prioritized price stability and stable operations of payment and settlement systems. The Bank of Japan has held interest rates below zero (negative interest rates) in a drastic attempt to revitalize the economy. Negative interest rates allow individuals to get paid to borrow money, but investors are disincentivised to deposit funds as this will incur a charge.
CENTRAL BANK RESPONSIBILITIES
Central banks have been established to fulfil a mandate in order to serve the public interest. While responsibilities may differ between countries, the main responsibilities include the following:
1) Achieve and maintain price stability: Central banks are tasked with protecting the value of their currency. This is done by maintaining a modest level of inflation in the economy.
2) Promoting financial system stability: Central banks subject commercial banks to a series of stress testing to reduce systemic risk in the financial sector.
3) Fostering balanced and sustainable growth in an economy: In general, there are two main avenues in which a country can stimulate its economy. These are through Fiscal policy (government spending) or monetary policy (central bank intervention). When governments have exhausted their budgets, central banks are still able to initiate monetary policy in an attempt to stimulate the economy.
4) Supervising and regulating financial institutions: Central banks are tasked with the duty of regulating and supervising commercial banks in the public interest.
5) Minimize unemployment: Apart from price stability and sustainable growth, central banks may have an interest in minimising unemployment. This is one of the goals from the Federal Reserve.
CENTRAL BANKS AND INTEREST RATES
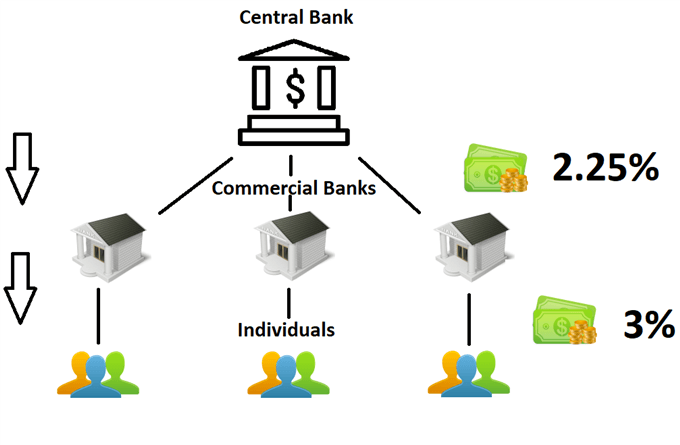
Central banks set the central bank interest rate, and all other interest rates that individuals experience on personal loans, home loans, credit cards etc, emanate from this base rate. The central bank interest rate is the interest rate that is charged to commercial banks looking to borrow money from the central bank on an overnight basis.
Commercial banks need to borrow funds from the central bank in order to comply with a modern form of banking called Fractional Reserve Banking. Banks accept deposits and make loans meaning they need to ensure that there is sufficient cash to service daily withdrawals, while lending the rest of depositors’ money to businesses and other investors that require cash. The bank generates revenue through this process by charging a higher interest rate on loans while paying lower rates to depositors.
Central banks will define the specific percentage of all depositors’ funds (reserve) that banks are required to set aside, and should the bank fall short of this, it can borrow from the central bank at the overnight rate, which is based on the annual central bank interest rate.
FX traders monitor central bank rates closely as they can have a significant impact on the forex market. Institutions and investors tend to follow yields (interest rates) and therefore, changes in these rates will result in traders channelling investment towards countries with higher interest rates.
HOW CENTRAL BANKS IMPACT THE FOREX MARKET
Forex traders often assess the language used by the chairman of the central bank to look for clues on whether the central bank is likely to increase or decrease interest rates. Language that is interpreted to suggest an increase/decrease in rates is referred to as Hawkish/Dovish. These subtle clues are referred to as “forward guidance” and have the potential to move the forex market.
Traders that believe the central bank is about to embark on an interest rate hiking cycle will place a long trade in favour of that currency, while traders anticipating a dovish stance from the central bank will look to short the currency.
For more information on this mechanism, read, “Interest Rates and the Forex Market”
Movements in central bank interest rates present traders with opportunities to trade based on the interest rate differential between two country’s currencies via a carry trade. Carry traders look to receive overnight interest for trading a high yielding currency against a low yielding currency.