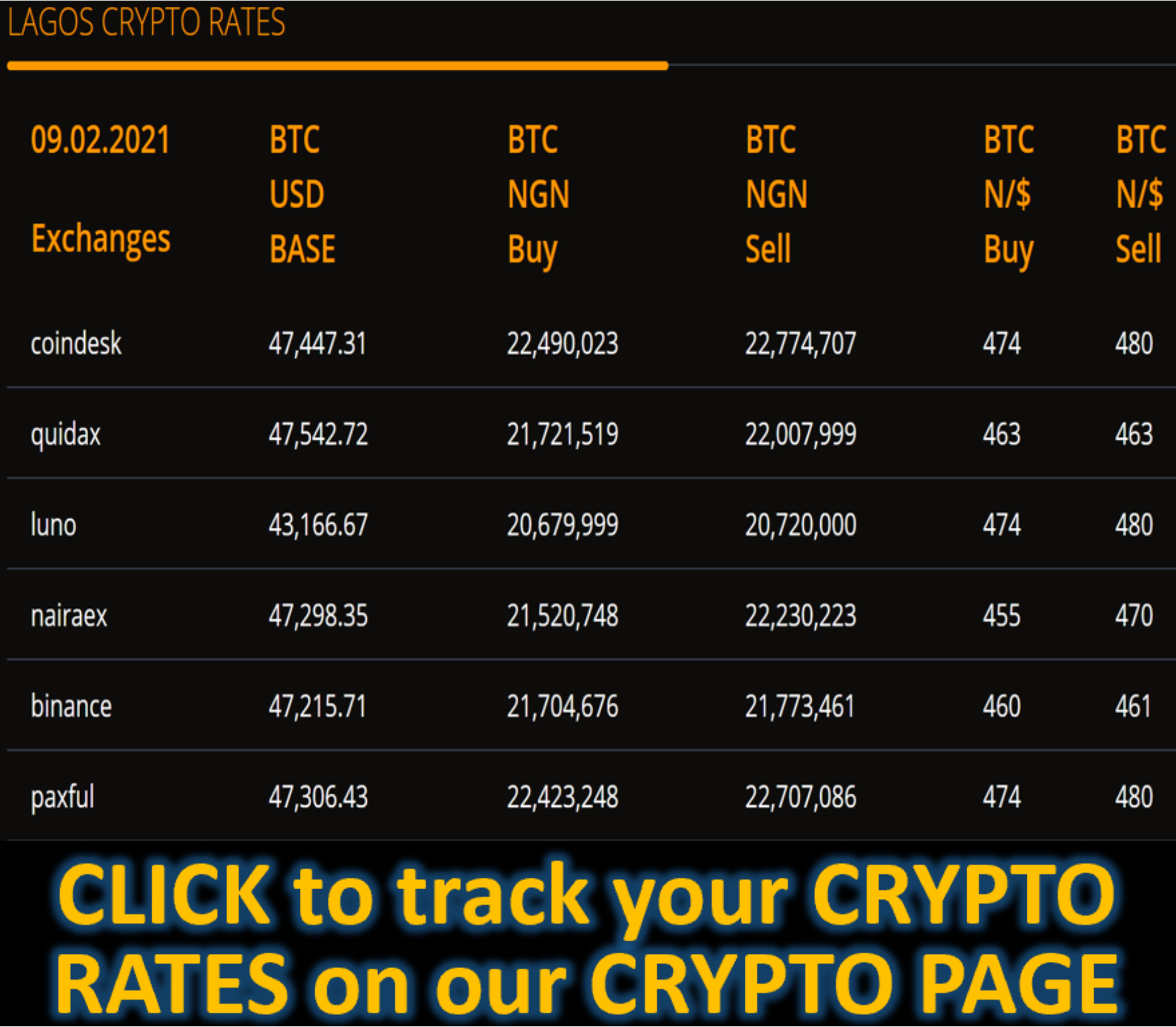
Market News
Central Bank of Nigeria Macroeconomic Outlook for Nigeria - PROSHARE
The Nigerian economy-maintained growth at a slower pace in 2023 despite facing global and domestic headwinds. Gross Domestic Product (GDP) growth decelerated to 2.74% from 3.40% and 3.10% recorded in 2021 and 2022, respectively, indicating a continued decline in annual output growth following the recovery from the COVID-19 pandemic. The growth performance was shaped by the adverse effects of supply chain disruptions (occasioned by the protracted Russia-Ukraine war), elevated inflation, and domestic insecurity, significantly reducing food production. Furthermore, Premium Motor Spirit (PMS) subsidy removal, foreign exchange reforms, longstanding infrastructural deficits, and global policy rate hikes weighed on growth outcomes.
Despite these challenges, the economy remained resilient, supported mainly by private consumption, which accounted for about two-thirds of output. Headline inflation remained elevated, rising from 21.34% in 2022 to 28.92% in 2023, owing to significant supply-side shocks from both global and domestic sources. The major drivers of inflation during the year included adverse spillovers from supply chain disruptions, higher energy and food prices due to the removal of PMS subsidies, exchange rate reforms, and widespread insecurity.