Market News
China suspends some critical mineral export curbs to the U.S. as trade truce takes hold - CNBC
Key Points
- China suspended export restrictions on several rare earth elements, processing technologies, lithium battery materials, and other items announced on Oct. 9, 2025.
- The rollback also extended to curbs on gallium, germanium, antimony and other super-hard materials, which dated back to December 2024.
- The easing of export restrictions signals progress after Xi and Trump’s Oct. 30 meeting in Busan.
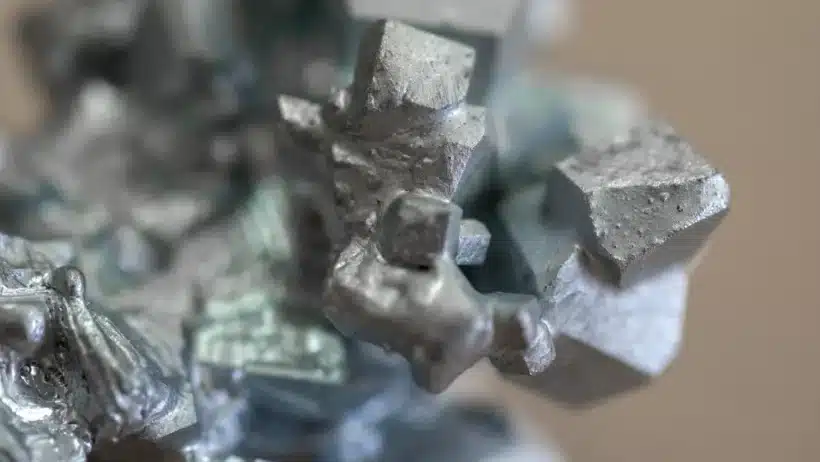
China has rolled back a number of restrictions on its export of critical minerals and rare earth materials to the United States, in a sign that a trade truce between the world’s two largest economies is holding.
China’s Ministry of Commerce said Friday that it would suspend some export controls on critical minerals used in military hardware, semiconductors and other high-tech industries for a year.
The suspended restrictions, first imposed on Oct. 9, include limits on the export of certain rare earth elements, lithium battery materials, and processing technologies.
The export relaxations follow talks between U.S. President Donald Trump and Chinese President Xi Jinping in Busan, South Korea, on Oct. 30.
Beijing also reversed retaliatory curbs on exports of gallium, germanium, antimony and other so-called super-hard materials such as synthetic diamonds and boron nitrides. Those measures, introduced in December 2024, were widely seen as retaliation for Washington’s expanded semiconductor export restrictions on China.
China classifies such materials as “dual-use items,” meaning they can be used for both civilian and military purposes.
Beyond military applications, these critical minerals are used across the semiconductor industry and other high-tech sectors – sectors at the heart of U.S.-China trade tensions.
Beijing has also suspended the stricter end-user and end-use verification checks for exports of dual-use graphite to the U.S., which were imposed in December 2024 alongside the broader export ban.
China dominates global production of most critical minerals and rare earth elements and has increasingly used its export policies as leverage in trade disputes.
As part of the latest China-U.S. trade deal, the U.S. has agreed to several concessions, including lowering tariffs on Chinese imports by 10 percentage points, and suspending Trump’s heightened “reciprocal tariffs” on Chinese imports until Nov. 10, 2026.
The U.S. will also postpone a rule announced Sept. 29 that would have blacklisted majority-owned subsidiaries of Chinese companies on its entity list.