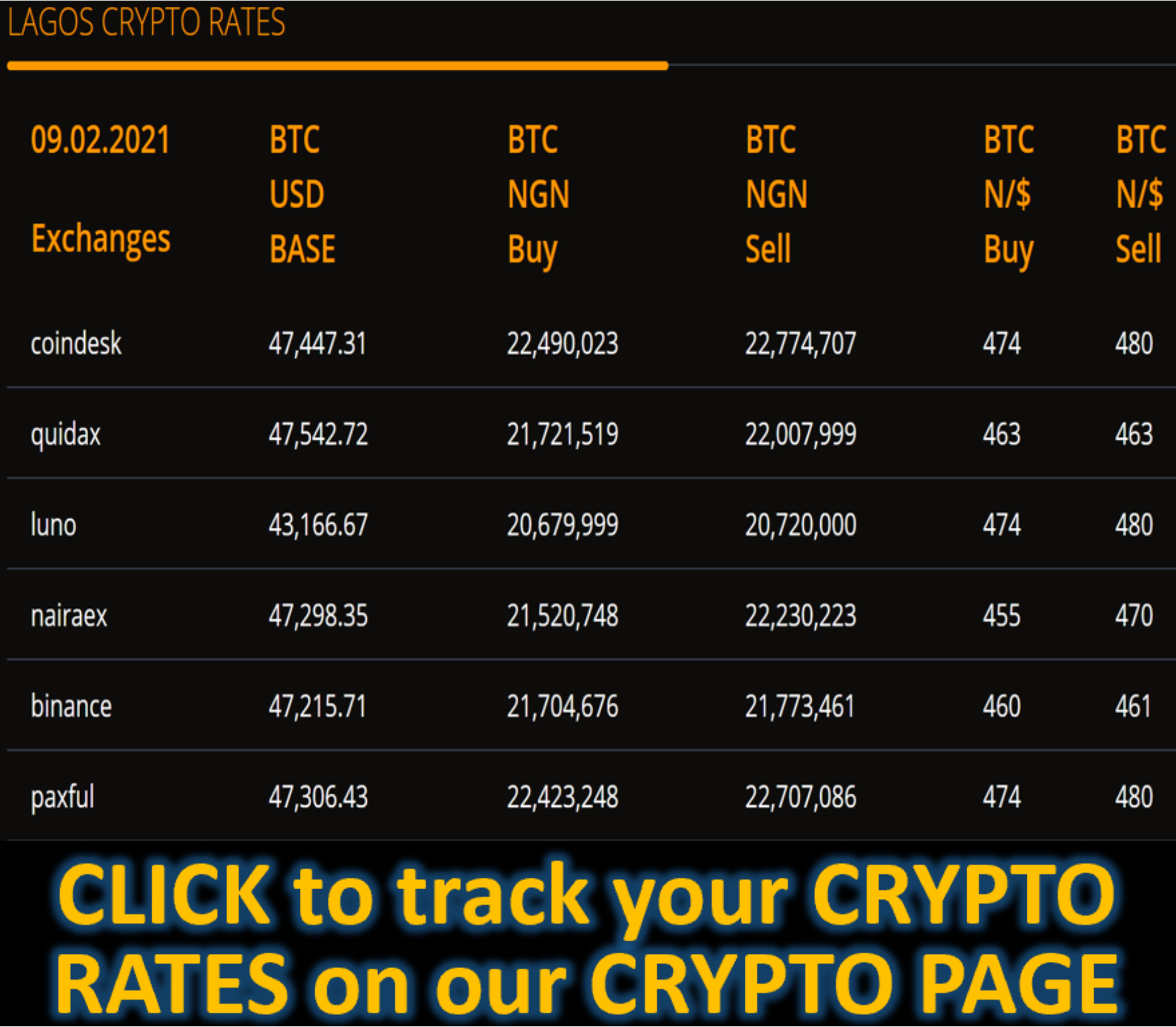
Market News
University tuition fees to increase in England for first time in eight years - SKY NEWS
Fees have been frozen at an annual level of £9,250 since the 2017/18 academic year but Education Secretary Bridget Phillipson has now confirmed they will rise from April 2025.
By Alix Culbertson and Faye Brown, political reporters
University tuition fees in England will increase for the first time in eight years, the education secretary has announced.
Fees have been frozen at an annual level of £9,250 since the 2017/18 academic year.
Education Secretary Bridget Phillipson said the maximum cap will now rise in line with inflation from April 2025.
That will increase the cost of tuition to £9,535 next year - a rise of £285.
Ms Phillipson also announced a rise in maximum maintenance loans so they will now increase in line with inflation, giving an increase of £414 a year to help students with living costs.
Sir Keir Starmer had pledged to abolish tuition fees when he stood to be Labour leader in 2020.
However, the prime minister rowed back on that promise early last year, saying it was no longer affordable because of the "different financial situation" the country was in, and he was choosing to prioritise the NHS.
However, at the time he said Labour would set out a "fairer solution" for students if they won the election.
The change comes as universities have been dealing with a funding crisis, largely driven by a huge drop in overseas students.
Rules brought in by Rishi Sunak's government made it harder for international students, who pay higher fees than British ones, to bring their families with them to the UK.
Universities have been pleading for more investment, but Ms Phillipson said recently institutes should seek to manage their own budgets before hoping for a bailout from the taxpayer.
When she was in opposition, she also touted the idea of reducing the monthly repayments "for every single graduate" by changing how the loan is paid back.
Writing in The Times in June 2023, she said: "Reworking the present system gives scope for a month-on-month tax cut for graduates, putting money back in people's pockets when they most need it."
However, the idea did not make it into Labour's 2024 manifesto, which only says that "the current higher education funding settlement does not work for the taxpayer, universities, staff, or students".
It adds: "Labour will act to create a secure future for higher education and the opportunities it creates across the UK."
Independent MP Zarah Sultana, who lost the Labour whip after rebelling over the two-child benefit cap, called the latest development "wrong".
"It's time to abolish tuition fees and cancel student debt because education is a public good, not a commodity," she posted on X.
'Maintenance loans bigger issue'
However, money saving expert Martin Lewis said higher fees will not necessarily lead to students facing higher yearly repayments, as that "solely depends on what you earn not on what you borrow".
In a thread on X, he said a more damaging policy was the Tories' decision last year to drop the salary threshold at which repayments must be made - from £27,000 to £25,000 - and increase the time to clear the loan before it is written off, from 30 to 40 years.
He said: "Increasing tuition fees will only see those who clear the loan in full over the 40yrs pay more. That is generally mid-high to higher earning university leavers only, so the cost of increasing them will generally be born by the more affluent."
Lewis added that a bigger problem for students is the fact maintenance loans "aren't big enough" and "have not kept pace with inflation".
University fees of £1,000 per year were first introduced by the Labour government in 1998, going up to £3,000 in 2006.
The coalition government then tripled the amount to £9,000 in 2012, sparking a huge backlash, particularly against the Lib Dems who had vowed to scrap fees in the 2010 general election campaign.
Since then, there have been further changes to student finance such as the abolition of maintenance grants and NHS bursaries, moving student support increasingly away from non-repayable grants and towards loans.